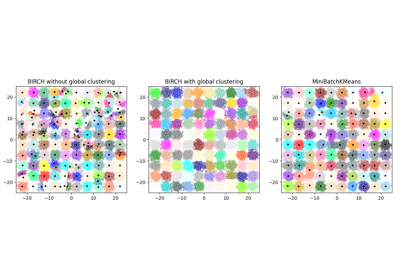
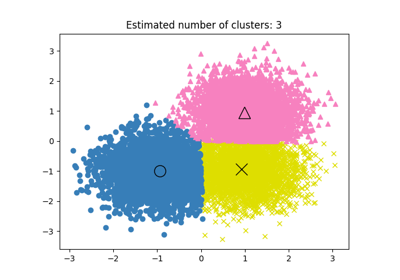
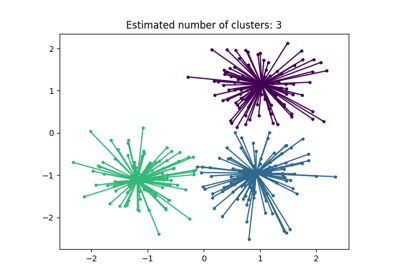
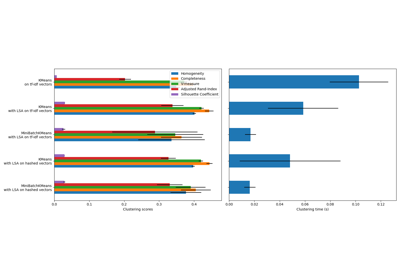
Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
Comparison of the K-Means and MiniBatchKMeans clustering algorithms#
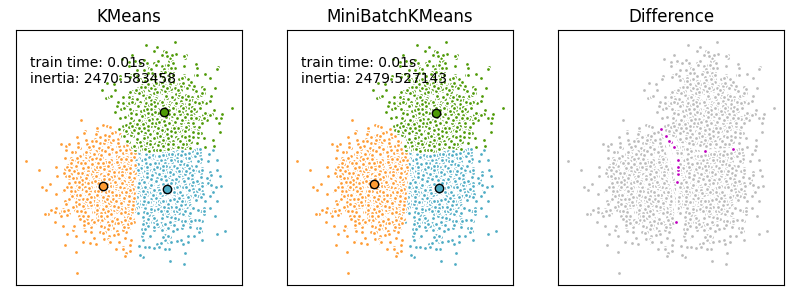
We want to compare the performance of the MiniBatchKMeans and KMeans: the MiniBatchKMeans is faster, but gives slightly different results (see Mini Batch K-Means).
We will cluster a set of data, first with KMeans and then with MiniBatchKMeans, and plot the results. We will also plot the points that are labelled differently between the two algorithms.
Generate the data#
We start by generating the blobs of data to be clustered.
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
np.random.seed(0)
batch_size = 45
centers = [[1, 1], [-1, -1], [1, -1]]
n_clusters = len(centers)
X, labels_true = make_blobs(n_samples=3000, centers=centers, cluster_std=0.7)
Compute clustering with KMeans#
Compute clustering with MiniBatchKMeans#
from sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchKMeans
mbk = MiniBatchKMeans(
init="k-means++",
n_clusters=3,
batch_size=batch_size,
n_init=10,
max_no_improvement=10,
verbose=0,
)
t0 = time.time()
mbk.fit(X)
t_mini_batch = time.time() - t0
Establishing parity between clusters#
We want to have the same color for the same cluster from both the MiniBatchKMeans and the KMeans algorithm. Let’s pair the cluster centers per closest one.
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances_argmin
k_means_cluster_centers = k_means.cluster_centers_
order = pairwise_distances_argmin(k_means.cluster_centers_, mbk.cluster_centers_)
mbk_means_cluster_centers = mbk.cluster_centers_[order]
k_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, k_means_cluster_centers)
mbk_means_labels = pairwise_distances_argmin(X, mbk_means_cluster_centers)
Plotting the results#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.02, right=0.98, bottom=0.05, top=0.9)
colors = ["#4EACC5", "#FF9C34", "#4E9A06"]
# KMeans
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 1)
for k, col in zip(range(n_clusters), colors):
my_members = k_means_labels == k
cluster_center = k_means_cluster_centers[k]
ax.plot(X[my_members, 0], X[my_members, 1], "w", markerfacecolor=col, marker=".")
ax.plot(
cluster_center[0],
cluster_center[1],
"o",
markerfacecolor=col,
markeredgecolor="k",
markersize=6,
)
ax.set_title("KMeans")
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
plt.text(-3.5, 1.8, "train time: %.2fs\ninertia: %f" % (t_batch, k_means.inertia_))
# MiniBatchKMeans
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 2)
for k, col in zip(range(n_clusters), colors):
my_members = mbk_means_labels == k
cluster_center = mbk_means_cluster_centers[k]
ax.plot(X[my_members, 0], X[my_members, 1], "w", markerfacecolor=col, marker=".")
ax.plot(
cluster_center[0],
cluster_center[1],
"o",
markerfacecolor=col,
markeredgecolor="k",
markersize=6,
)
ax.set_title("MiniBatchKMeans")
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
plt.text(-3.5, 1.8, "train time: %.2fs\ninertia: %f" % (t_mini_batch, mbk.inertia_))
# Initialize the different array to all False
different = mbk_means_labels == 4
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 3, 3)
for k in range(n_clusters):
different += (k_means_labels == k) != (mbk_means_labels == k)
identical = np.logical_not(different)
ax.plot(X[identical, 0], X[identical, 1], "w", markerfacecolor="#bbbbbb", marker=".")
ax.plot(X[different, 0], X[different, 1], "w", markerfacecolor="m", marker=".")
ax.set_title("Difference")
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.156 seconds)
Related examples
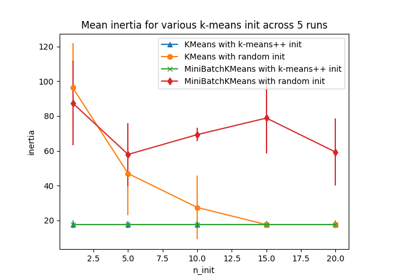
Empirical evaluation of the impact of k-means initialization