Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
Prediction Intervals for Gradient Boosting Regression#
This example shows how quantile regression can be used to create prediction intervals.
Generate some data for a synthetic regression problem by applying the function f to uniformly sampled random inputs.
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
def f(x):
"""The function to predict."""
return x * np.sin(x)
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
X = np.atleast_2d(rng.uniform(0, 10.0, size=1000)).T
expected_y = f(X).ravel()
To make the problem interesting, we generate observations of the target y as the sum of a deterministic term computed by the function f and a random noise term that follows a centered log-normal. To make this even more interesting we consider the case where the amplitude of the noise depends on the input variable x (heteroscedastic noise).
The lognormal distribution is non-symmetric and long tailed: observing large outliers is likely but it is impossible to observe small outliers.
sigma = 0.5 + X.ravel() / 10
noise = rng.lognormal(sigma=sigma) - np.exp(sigma**2 / 2)
y = expected_y + noise
Split into train, test datasets:
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
Fitting non-linear quantile and least squares regressors#
Fit gradient boosting models trained with the quantile loss and alpha=0.05, 0.5, 0.95.
The models obtained for alpha=0.05 and alpha=0.95 produce a 90% confidence interval (95% - 5% = 90%).
The model trained with alpha=0.5 produces a regression of the median: on average, there should be the same number of target observations above and below the predicted values.
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_pinball_loss, mean_squared_error
all_models = {}
common_params = dict(
learning_rate=0.05,
n_estimators=200,
max_depth=2,
min_samples_leaf=9,
min_samples_split=9,
)
for alpha in [0.05, 0.5, 0.95]:
gbr = GradientBoostingRegressor(loss="quantile", alpha=alpha, **common_params)
all_models["q %1.2f" % alpha] = gbr.fit(X_train, y_train)
Notice that HistGradientBoostingRegressor is much
faster than GradientBoostingRegressor starting with
intermediate datasets (n_samples >= 10_000), which is not the case of the
present example.
For the sake of comparison, we also fit a baseline model trained with the usual (mean) squared error (MSE).
gbr_ls = GradientBoostingRegressor(loss="squared_error", **common_params)
all_models["mse"] = gbr_ls.fit(X_train, y_train)
Create an evenly spaced evaluation set of input values spanning the [0, 10] range.
xx = np.atleast_2d(np.linspace(0, 10, 1000)).T
Plot the true conditional mean function f, the predictions of the conditional mean (loss equals squared error), the conditional median and the conditional 90% interval (from 5th to 95th conditional percentiles).
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
y_pred = all_models["mse"].predict(xx)
y_lower = all_models["q 0.05"].predict(xx)
y_upper = all_models["q 0.95"].predict(xx)
y_med = all_models["q 0.50"].predict(xx)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.plot(xx, f(xx), "g:", linewidth=3, label=r"$f(x) = x\,\sin(x)$")
plt.plot(X_test, y_test, "b.", markersize=10, label="Test observations")
plt.plot(xx, y_med, "r-", label="Predicted median")
plt.plot(xx, y_pred, "r-", label="Predicted mean")
plt.plot(xx, y_upper, "k-")
plt.plot(xx, y_lower, "k-")
plt.fill_between(
xx.ravel(), y_lower, y_upper, alpha=0.4, label="Predicted 90% interval"
)
plt.xlabel("$x$")
plt.ylabel("$f(x)$")
plt.ylim(-10, 25)
plt.legend(loc="upper left")
plt.show()
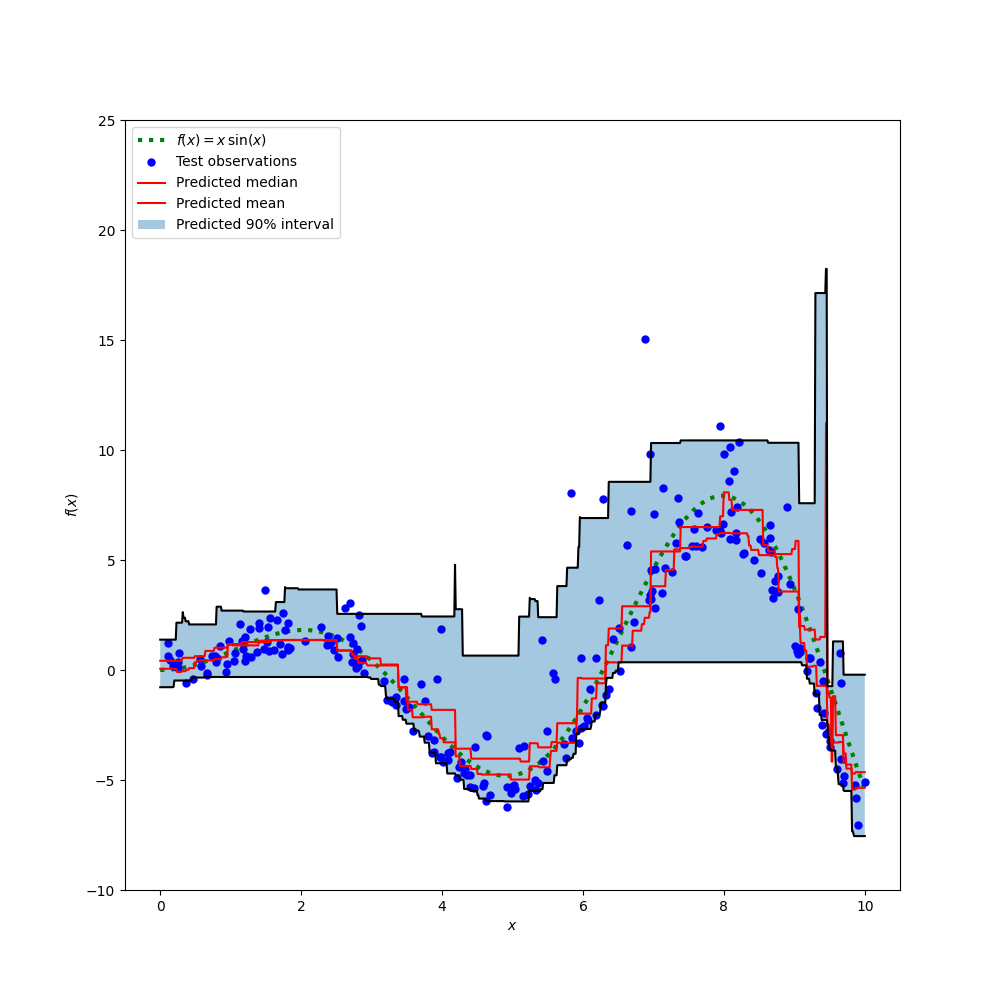
Comparing the predicted median with the predicted mean, we note that the median is on average below the mean as the noise is skewed towards high values (large outliers). The median estimate also seems to be smoother because of its natural robustness to outliers.
Also observe that the inductive bias of gradient boosting trees is unfortunately preventing our 0.05 quantile to fully capture the sinoisoidal shape of the signal, in particular around x=8. Tuning hyper-parameters can reduce this effect as shown in the last part of this notebook.
Analysis of the error metrics#
Measure the models with mean_squared_error and
mean_pinball_loss metrics on the training dataset.
import pandas as pd
def highlight_min(x):
x_min = x.min()
return ["font-weight: bold" if v == x_min else "" for v in x]
results = []
for name, gbr in sorted(all_models.items()):
metrics = {"model": name}
y_pred = gbr.predict(X_train)
for alpha in [0.05, 0.5, 0.95]:
metrics["pbl=%1.2f" % alpha] = mean_pinball_loss(y_train, y_pred, alpha=alpha)
metrics["MSE"] = mean_squared_error(y_train, y_pred)
results.append(metrics)
pd.DataFrame(results).set_index("model").style.apply(highlight_min)
One column shows all models evaluated by the same metric. The minimum number on a column should be obtained when the model is trained and measured with the same metric. This should be always the case on the training set if the training converged.
Note that because the target distribution is asymmetric, the expected conditional mean and conditional median are significantly different and therefore one could not use the squared error model get a good estimation of the conditional median nor the converse.
If the target distribution were symmetric and had no outliers (e.g. with a Gaussian noise), then median estimator and the least squares estimator would have yielded similar predictions.
We then do the same on the test set.
results = []
for name, gbr in sorted(all_models.items()):
metrics = {"model": name}
y_pred = gbr.predict(X_test)
for alpha in [0.05, 0.5, 0.95]:
metrics["pbl=%1.2f" % alpha] = mean_pinball_loss(y_test, y_pred, alpha=alpha)
metrics["MSE"] = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
results.append(metrics)
pd.DataFrame(results).set_index("model").style.apply(highlight_min)
Errors are higher meaning the models slightly overfitted the data. It still shows that the best test metric is obtained when the model is trained by minimizing this same metric.
Note that the conditional median estimator is competitive with the squared error estimator in terms of MSE on the test set: this can be explained by the fact the squared error estimator is very sensitive to large outliers which can cause significant overfitting. This can be seen on the right hand side of the previous plot. The conditional median estimator is biased (underestimation for this asymmetric noise) but is also naturally robust to outliers and overfits less.
Calibration of the confidence interval#
We can also evaluate the ability of the two extreme quantile estimators at producing a well-calibrated conditional 90%-confidence interval.
To do this we can compute the fraction of observations that fall between the predictions:
def coverage_fraction(y, y_low, y_high):
return np.mean(np.logical_and(y >= y_low, y <= y_high))
coverage_fraction(
y_train,
all_models["q 0.05"].predict(X_train),
all_models["q 0.95"].predict(X_train),
)
0.9
On the training set the calibration is very close to the expected coverage value for a 90% confidence interval.
coverage_fraction(
y_test, all_models["q 0.05"].predict(X_test), all_models["q 0.95"].predict(X_test)
)
0.868
On the test set, the estimated confidence interval is slightly too narrow. Note, however, that we would need to wrap those metrics in a cross-validation loop to assess their variability under data resampling.
Tuning the hyper-parameters of the quantile regressors#
In the plot above, we observed that the 5th percentile regressor seems to underfit and could not adapt to sinusoidal shape of the signal.
The hyper-parameters of the model were approximately hand-tuned for the median regressor and there is no reason that the same hyper-parameters are suitable for the 5th percentile regressor.
To confirm this hypothesis, we tune the hyper-parameters of a new regressor of the 5th percentile by selecting the best model parameters by cross-validation on the pinball loss with alpha=0.05:
from sklearn.experimental import enable_halving_search_cv # noqa
from sklearn.model_selection import HalvingRandomSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import make_scorer
from pprint import pprint
param_grid = dict(
learning_rate=[0.05, 0.1, 0.2],
max_depth=[2, 5, 10],
min_samples_leaf=[1, 5, 10, 20],
min_samples_split=[5, 10, 20, 30, 50],
)
alpha = 0.05
neg_mean_pinball_loss_05p_scorer = make_scorer(
mean_pinball_loss,
alpha=alpha,
greater_is_better=False, # maximize the negative loss
)
gbr = GradientBoostingRegressor(loss="quantile", alpha=alpha, random_state=0)
search_05p = HalvingRandomSearchCV(
gbr,
param_grid,
resource="n_estimators",
max_resources=250,
min_resources=50,
scoring=neg_mean_pinball_loss_05p_scorer,
n_jobs=2,
random_state=0,
).fit(X_train, y_train)
pprint(search_05p.best_params_)
{'learning_rate': 0.2,
'max_depth': 2,
'min_samples_leaf': 20,
'min_samples_split': 10,
'n_estimators': 150}
We observe that the hyper-parameters that were hand-tuned for the median regressor are in the same range as the hyper-parameters suitable for the 5th percentile regressor.
Let’s now tune the hyper-parameters for the 95th percentile regressor. We
need to redefine the scoring metric used to select the best model, along
with adjusting the alpha parameter of the inner gradient boosting estimator
itself:
from sklearn.base import clone
alpha = 0.95
neg_mean_pinball_loss_95p_scorer = make_scorer(
mean_pinball_loss,
alpha=alpha,
greater_is_better=False, # maximize the negative loss
)
search_95p = clone(search_05p).set_params(
estimator__alpha=alpha,
scoring=neg_mean_pinball_loss_95p_scorer,
)
search_95p.fit(X_train, y_train)
pprint(search_95p.best_params_)
{'learning_rate': 0.05,
'max_depth': 2,
'min_samples_leaf': 5,
'min_samples_split': 20,
'n_estimators': 150}
The result shows that the hyper-parameters for the 95th percentile regressor identified by the search procedure are roughly in the same range as the hand- tuned hyper-parameters for the median regressor and the hyper-parameters identified by the search procedure for the 5th percentile regressor. However, the hyper-parameter searches did lead to an improved 90% confidence interval that is comprised by the predictions of those two tuned quantile regressors. Note that the prediction of the upper 95th percentile has a much coarser shape than the prediction of the lower 5th percentile because of the outliers:
y_lower = search_05p.predict(xx)
y_upper = search_95p.predict(xx)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.plot(xx, f(xx), "g:", linewidth=3, label=r"$f(x) = x\,\sin(x)$")
plt.plot(X_test, y_test, "b.", markersize=10, label="Test observations")
plt.plot(xx, y_upper, "k-")
plt.plot(xx, y_lower, "k-")
plt.fill_between(
xx.ravel(), y_lower, y_upper, alpha=0.4, label="Predicted 90% interval"
)
plt.xlabel("$x$")
plt.ylabel("$f(x)$")
plt.ylim(-10, 25)
plt.legend(loc="upper left")
plt.title("Prediction with tuned hyper-parameters")
plt.show()
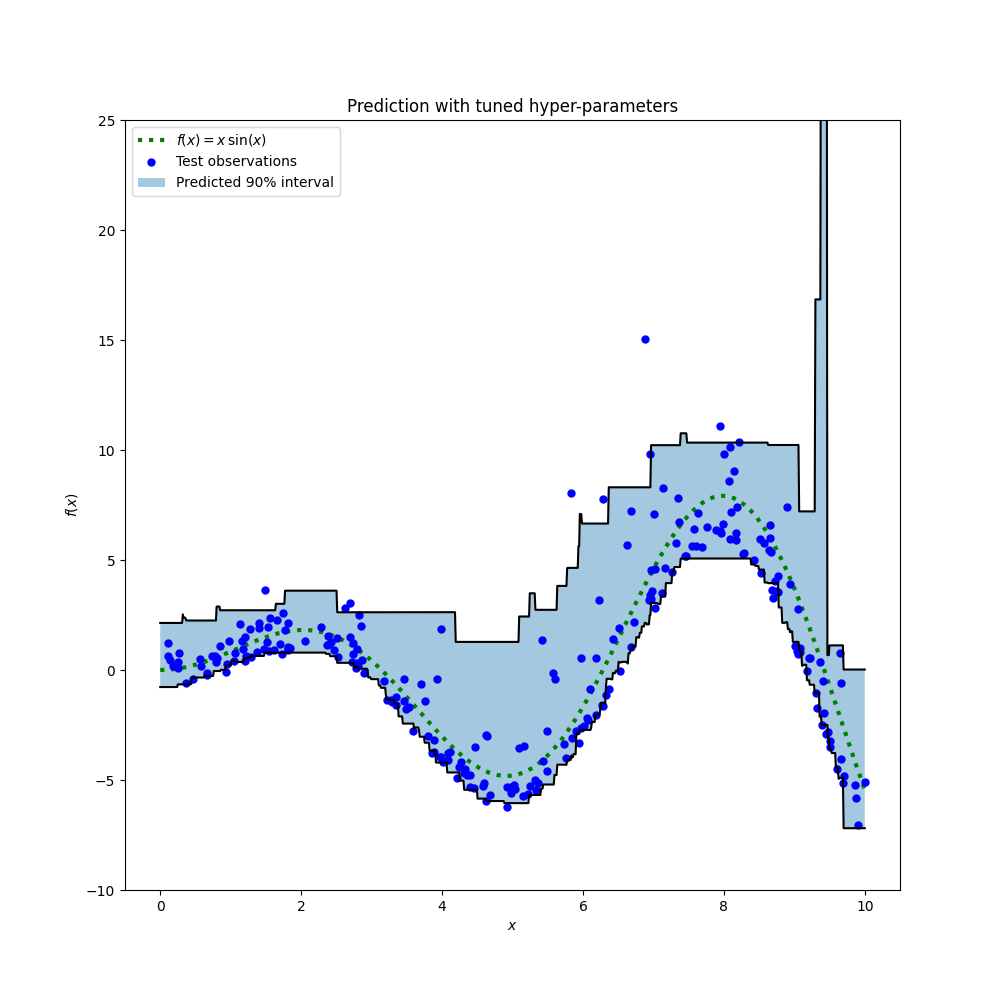
The plot looks qualitatively better than for the untuned models, especially for the shape of the of lower quantile.
We now quantitatively evaluate the joint-calibration of the pair of estimators:
coverage_fraction(y_train, search_05p.predict(X_train), search_95p.predict(X_train))
0.9026666666666666
coverage_fraction(y_test, search_05p.predict(X_test), search_95p.predict(X_test))
0.796
The calibration of the tuned pair is sadly not better on the test set: the width of the estimated confidence interval is still too narrow.
Again, we would need to wrap this study in a cross-validation loop to better assess the variability of those estimates.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 9.425 seconds)
Related examples
Gaussian Processes regression: basic introductory example