Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
Varying regularization in Multi-layer Perceptron#
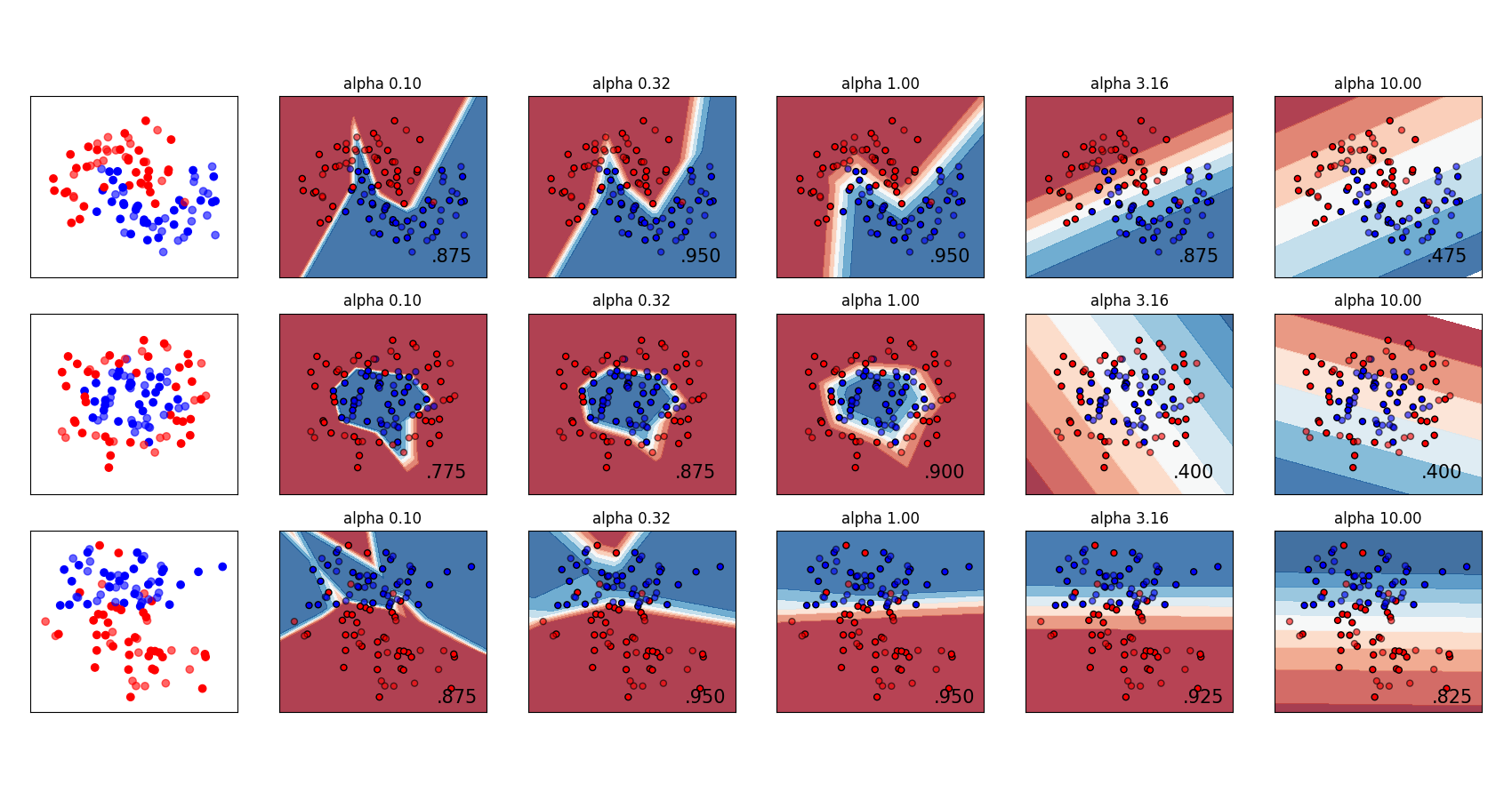
A comparison of different values for regularization parameter ‘alpha’ on synthetic datasets. The plot shows that different alphas yield different decision functions.
Alpha is a parameter for regularization term, aka penalty term, that combats overfitting by constraining the size of the weights. Increasing alpha may fix high variance (a sign of overfitting) by encouraging smaller weights, resulting in a decision boundary plot that appears with lesser curvatures. Similarly, decreasing alpha may fix high bias (a sign of underfitting) by encouraging larger weights, potentially resulting in a more complicated decision boundary.
# Author: Issam H. Laradji
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
from sklearn.datasets import make_circles, make_classification, make_moons
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
h = 0.02 # step size in the mesh
alphas = np.logspace(-1, 1, 5)
classifiers = []
names = []
for alpha in alphas:
classifiers.append(
make_pipeline(
StandardScaler(),
MLPClassifier(
solver="lbfgs",
alpha=alpha,
random_state=1,
max_iter=2000,
early_stopping=True,
hidden_layer_sizes=[10, 10],
),
)
)
names.append(f"alpha {alpha:.2f}")
X, y = make_classification(
n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=2, random_state=0, n_clusters_per_class=1
)
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
X += 2 * rng.uniform(size=X.shape)
linearly_separable = (X, y)
datasets = [
make_moons(noise=0.3, random_state=0),
make_circles(noise=0.2, factor=0.5, random_state=1),
linearly_separable,
]
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(17, 9))
i = 1
# iterate over datasets
for X, y in datasets:
# split into training and test part
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.4, random_state=42
)
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 0.5, X[:, 0].max() + 0.5
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 0.5, X[:, 1].max() + 0.5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
# just plot the dataset first
cm = plt.cm.RdBu
cm_bright = ListedColormap(["#FF0000", "#0000FF"])
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
# Plot the training points
ax.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c=y_train, cmap=cm_bright)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, cmap=cm_bright, alpha=0.6)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
i += 1
# iterate over classifiers
for name, clf in zip(names, classifiers):
ax = plt.subplot(len(datasets), len(classifiers) + 1, i)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
score = clf.score(X_test, y_test)
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, x_max] x [y_min, y_max].
if hasattr(clf, "decision_function"):
Z = clf.decision_function(np.column_stack([xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]))
else:
Z = clf.predict_proba(np.column_stack([xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]))[:, 1]
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
ax.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=cm, alpha=0.8)
# Plot also the training points
ax.scatter(
X_train[:, 0],
X_train[:, 1],
c=y_train,
cmap=cm_bright,
edgecolors="black",
s=25,
)
# and testing points
ax.scatter(
X_test[:, 0],
X_test[:, 1],
c=y_test,
cmap=cm_bright,
alpha=0.6,
edgecolors="black",
s=25,
)
ax.set_xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
ax.set_ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
ax.set_xticks(())
ax.set_yticks(())
ax.set_title(name)
ax.text(
xx.max() - 0.3,
yy.min() + 0.3,
f"{score:.3f}".lstrip("0"),
size=15,
horizontalalignment="right",
)
i += 1
figure.subplots_adjust(left=0.02, right=0.98)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.924 seconds)
Related examples
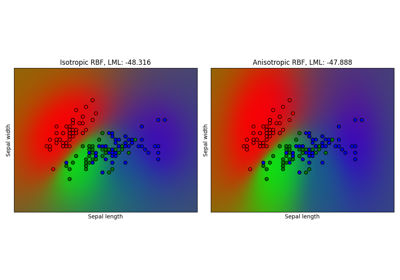
Gaussian process classification (GPC) on iris dataset
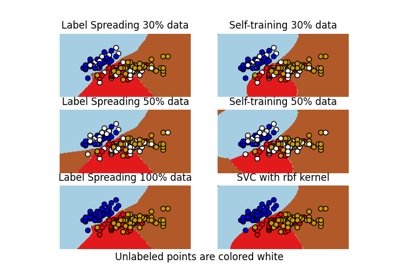
Decision boundary of semi-supervised classifiers versus SVM on the Iris dataset