Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
Monotonic Constraints#
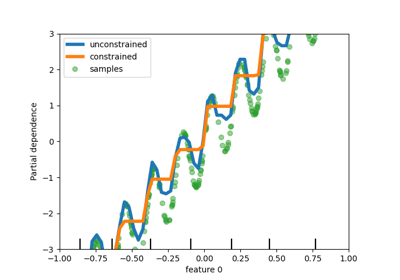
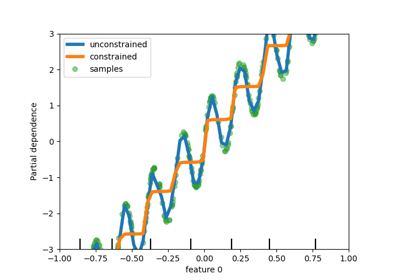
This example illustrates the effect of monotonic constraints on a gradient boosting estimator.
We build an artificial dataset where the target value is in general positively correlated with the first feature (with some random and non-random variations), and in general negatively correlated with the second feature.
By imposing a monotonic increase or a monotonic decrease constraint, respectively, on the features during the learning process, the estimator is able to properly follow the general trend instead of being subject to the variations.
This example was inspired by the XGBoost documentation.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import HistGradientBoostingRegressor
from sklearn.inspection import PartialDependenceDisplay
rng = np.random.RandomState(0)
n_samples = 1000
f_0 = rng.rand(n_samples)
f_1 = rng.rand(n_samples)
X = np.c_[f_0, f_1]
noise = rng.normal(loc=0.0, scale=0.01, size=n_samples)
# y is positively correlated with f_0, and negatively correlated with f_1
y = 5 * f_0 + np.sin(10 * np.pi * f_0) - 5 * f_1 - np.cos(10 * np.pi * f_1) + noise
Fit a first model on this dataset without any constraints.
gbdt_no_cst = HistGradientBoostingRegressor()
gbdt_no_cst.fit(X, y)
Fit a second model on this dataset with monotonic increase (1) and a monotonic decrease (-1) constraints, respectively.
gbdt_with_monotonic_cst = HistGradientBoostingRegressor(monotonic_cst=[1, -1])
gbdt_with_monotonic_cst.fit(X, y)
Let’s display the partial dependence of the predictions on the two features.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
disp = PartialDependenceDisplay.from_estimator(
gbdt_no_cst,
X,
features=[0, 1],
feature_names=(
"First feature",
"Second feature",
),
line_kw={"linewidth": 4, "label": "unconstrained", "color": "tab:blue"},
ax=ax,
)
PartialDependenceDisplay.from_estimator(
gbdt_with_monotonic_cst,
X,
features=[0, 1],
line_kw={"linewidth": 4, "label": "constrained", "color": "tab:orange"},
ax=disp.axes_,
)
for f_idx in (0, 1):
disp.axes_[0, f_idx].plot(
X[:, f_idx], y, "o", alpha=0.3, zorder=-1, color="tab:green"
)
disp.axes_[0, f_idx].set_ylim(-6, 6)
plt.legend()
fig.suptitle("Monotonic constraints effect on partial dependences")
plt.show()
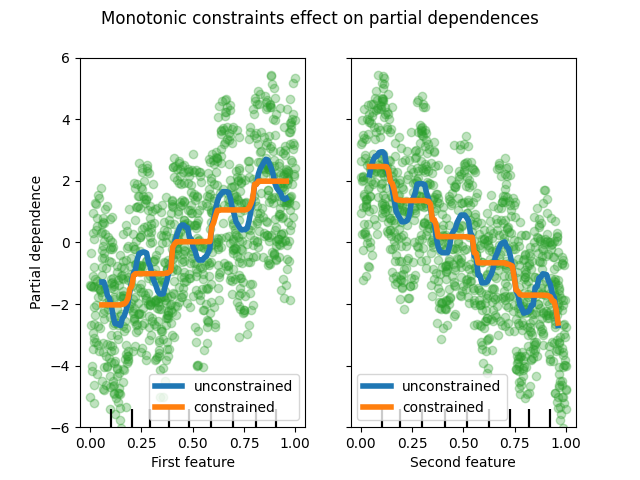
We can see that the predictions of the unconstrained model capture the oscillations of the data while the constrained model follows the general trend and ignores the local variations.
Using feature names to specify monotonic constraints#
Note that if the training data has feature names, it’s possible to specify the monotonic constraints by passing a dictionary:
import pandas as pd
X_df = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=["f_0", "f_1"])
gbdt_with_monotonic_cst_df = HistGradientBoostingRegressor(
monotonic_cst={"f_0": 1, "f_1": -1}
).fit(X_df, y)
np.allclose(
gbdt_with_monotonic_cst_df.predict(X_df), gbdt_with_monotonic_cst.predict(X)
)
True
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.594 seconds)
Related examples
Partial Dependence and Individual Conditional Expectation Plots