sklearn.model_selection.TimeSeriesSplit#
- class sklearn.model_selection.TimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=5, *, max_train_size=None, test_size=None, gap=0)[source]#
Time Series cross-validator.
Provides train/test indices to split time series data samples that are observed at fixed time intervals, in train/test sets. In each split, test indices must be higher than before, and thus shuffling in cross validator is inappropriate.
This cross-validation object is a variation of
KFold. In the kth split, it returns first k folds as train set and the (k+1)th fold as test set.Note that unlike standard cross-validation methods, successive training sets are supersets of those that come before them.
Read more in the User Guide.
For visualisation of cross-validation behaviour and comparison between common scikit-learn split methods refer to Visualizing cross-validation behavior in scikit-learn
New in version 0.18.
- Parameters:
- n_splitsint, default=5
Number of splits. Must be at least 2.
Changed in version 0.22:
n_splitsdefault value changed from 3 to 5.- max_train_sizeint, default=None
Maximum size for a single training set.
- test_sizeint, default=None
Used to limit the size of the test set. Defaults to
n_samples // (n_splits + 1), which is the maximum allowed value withgap=0.New in version 0.24.
- gapint, default=0
Number of samples to exclude from the end of each train set before the test set.
New in version 0.24.
Notes
The training set has size
i * n_samples // (n_splits + 1) + n_samples % (n_splits + 1)in theith split, with a test set of sizen_samples//(n_splits + 1)by default, wheren_samplesis the number of samples.Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> from sklearn.model_selection import TimeSeriesSplit >>> X = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [1, 2], [3, 4], [1, 2], [3, 4]]) >>> y = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) >>> tscv = TimeSeriesSplit() >>> print(tscv) TimeSeriesSplit(gap=0, max_train_size=None, n_splits=5, test_size=None) >>> for i, (train_index, test_index) in enumerate(tscv.split(X)): ... print(f"Fold {i}:") ... print(f" Train: index={train_index}") ... print(f" Test: index={test_index}") Fold 0: Train: index=[0] Test: index=[1] Fold 1: Train: index=[0 1] Test: index=[2] Fold 2: Train: index=[0 1 2] Test: index=[3] Fold 3: Train: index=[0 1 2 3] Test: index=[4] Fold 4: Train: index=[0 1 2 3 4] Test: index=[5] >>> # Fix test_size to 2 with 12 samples >>> X = np.random.randn(12, 2) >>> y = np.random.randint(0, 2, 12) >>> tscv = TimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=3, test_size=2) >>> for i, (train_index, test_index) in enumerate(tscv.split(X)): ... print(f"Fold {i}:") ... print(f" Train: index={train_index}") ... print(f" Test: index={test_index}") Fold 0: Train: index=[0 1 2 3 4 5] Test: index=[6 7] Fold 1: Train: index=[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7] Test: index=[8 9] Fold 2: Train: index=[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9] Test: index=[10 11] >>> # Add in a 2 period gap >>> tscv = TimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=3, test_size=2, gap=2) >>> for i, (train_index, test_index) in enumerate(tscv.split(X)): ... print(f"Fold {i}:") ... print(f" Train: index={train_index}") ... print(f" Test: index={test_index}") Fold 0: Train: index=[0 1 2 3] Test: index=[6 7] Fold 1: Train: index=[0 1 2 3 4 5] Test: index=[8 9] Fold 2: Train: index=[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7] Test: index=[10 11]
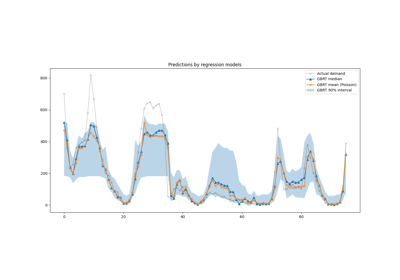
For a more extended example see Time-related feature engineering.
Methods
Get metadata routing of this object.
get_n_splits([X, y, groups])Returns the number of splitting iterations in the cross-validator.
split(X[, y, groups])Generate indices to split data into training and test set.
- get_metadata_routing()[source]#
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_n_splits(X=None, y=None, groups=None)[source]#
Returns the number of splitting iterations in the cross-validator.
- Parameters:
- Xobject
Always ignored, exists for compatibility.
- yobject
Always ignored, exists for compatibility.
- groupsobject
Always ignored, exists for compatibility.
- Returns:
- n_splitsint
Returns the number of splitting iterations in the cross-validator.
- split(X, y=None, groups=None)[source]#
Generate indices to split data into training and test set.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data, where
n_samplesis the number of samples andn_featuresis the number of features.- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
Always ignored, exists for compatibility.
- groupsarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
Always ignored, exists for compatibility.
- Yields:
- trainndarray
The training set indices for that split.
- testndarray
The testing set indices for that split.
Examples using sklearn.model_selection.TimeSeriesSplit#
Visualizing cross-validation behavior in scikit-learn