sklearn.utils.check_random_state#
- sklearn.utils.check_random_state(seed)[source]#
Turn seed into a np.random.RandomState instance.
- Parameters:
- seedNone, int or instance of RandomState
If seed is None, return the RandomState singleton used by np.random. If seed is an int, return a new RandomState instance seeded with seed. If seed is already a RandomState instance, return it. Otherwise raise ValueError.
- Returns:
numpy.random.RandomStateThe random state object based on
seedparameter.
Examples
>>> from sklearn.utils.validation import check_random_state >>> check_random_state(42) RandomState(MT19937) at 0x...
Examples using sklearn.utils.check_random_state#
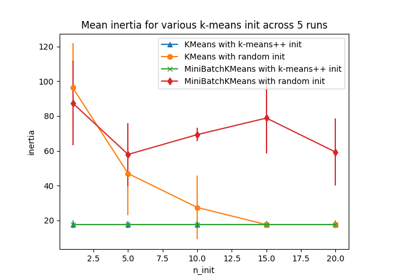
Empirical evaluation of the impact of k-means initialization
Empirical evaluation of the impact of k-means initialization

MNIST classification using multinomial logistic + L1
MNIST classification using multinomial logistic + L1