sklearn.preprocessing.RobustScaler#
- class sklearn.preprocessing.RobustScaler(*, with_centering=True, with_scaling=True, quantile_range=(25.0, 75.0), copy=True, unit_variance=False)[source]#
Scale features using statistics that are robust to outliers.
This Scaler removes the median and scales the data according to the quantile range (defaults to IQR: Interquartile Range). The IQR is the range between the 1st quartile (25th quantile) and the 3rd quartile (75th quantile).
Centering and scaling happen independently on each feature by computing the relevant statistics on the samples in the training set. Median and interquartile range are then stored to be used on later data using the
transformmethod.Standardization of a dataset is a common preprocessing for many machine learning estimators. Typically this is done by removing the mean and scaling to unit variance. However, outliers can often influence the sample mean / variance in a negative way. In such cases, using the median and the interquartile range often give better results. For an example visualization and comparison to other scalers, refer to Compare RobustScaler with other scalers.
New in version 0.17.
Read more in the User Guide.
- Parameters:
- with_centeringbool, default=True
If
True, center the data before scaling. This will causetransformto raise an exception when attempted on sparse matrices, because centering them entails building a dense matrix which in common use cases is likely to be too large to fit in memory.- with_scalingbool, default=True
If
True, scale the data to interquartile range.- quantile_rangetuple (q_min, q_max), 0.0 < q_min < q_max < 100.0, default=(25.0, 75.0)
Quantile range used to calculate
scale_. By default this is equal to the IQR, i.e.,q_minis the first quantile andq_maxis the third quantile.New in version 0.18.
- copybool, default=True
If
False, try to avoid a copy and do inplace scaling instead. This is not guaranteed to always work inplace; e.g. if the data is not a NumPy array or scipy.sparse CSR matrix, a copy may still be returned.- unit_variancebool, default=False
If
True, scale data so that normally distributed features have a variance of 1. In general, if the difference between the x-values ofq_maxandq_minfor a standard normal distribution is greater than 1, the dataset will be scaled down. If less than 1, the dataset will be scaled up.New in version 0.24.
- Attributes:
- center_array of floats
The median value for each feature in the training set.
- scale_array of floats
The (scaled) interquartile range for each feature in the training set.
New in version 0.17: scale_ attribute.
- n_features_in_int
Number of features seen during fit.
New in version 0.24.
- feature_names_in_ndarray of shape (
n_features_in_,) Names of features seen during fit. Defined only when
Xhas feature names that are all strings.New in version 1.0.
See also
robust_scaleEquivalent function without the estimator API.
sklearn.decomposition.PCAFurther removes the linear correlation across features with ‘whiten=True’.
Notes
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Median https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interquartile_range
Examples
>>> from sklearn.preprocessing import RobustScaler >>> X = [[ 1., -2., 2.], ... [ -2., 1., 3.], ... [ 4., 1., -2.]] >>> transformer = RobustScaler().fit(X) >>> transformer RobustScaler() >>> transformer.transform(X) array([[ 0. , -2. , 0. ], [-1. , 0. , 0.4], [ 1. , 0. , -1.6]])
Methods
fit(X[, y])Compute the median and quantiles to be used for scaling.
fit_transform(X[, y])Fit to data, then transform it.
get_feature_names_out([input_features])Get output feature names for transformation.
Get metadata routing of this object.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
Scale back the data to the original representation.
set_output(*[, transform])Set output container.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
transform(X)Center and scale the data.
- fit(X, y=None)[source]#
Compute the median and quantiles to be used for scaling.
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The data used to compute the median and quantiles used for later scaling along the features axis.
- yIgnored
Not used, present here for API consistency by convention.
- Returns:
- selfobject
Fitted scaler.
- fit_transform(X, y=None, **fit_params)[source]#
Fit to data, then transform it.
Fits transformer to
Xandywith optional parametersfit_paramsand returns a transformed version ofX.- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Input samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,) or (n_samples, n_outputs), default=None
Target values (None for unsupervised transformations).
- **fit_paramsdict
Additional fit parameters.
- Returns:
- X_newndarray array of shape (n_samples, n_features_new)
Transformed array.
- get_feature_names_out(input_features=None)[source]#
Get output feature names for transformation.
- Parameters:
- input_featuresarray-like of str or None, default=None
Input features.
If
input_featuresisNone, thenfeature_names_in_is used as feature names in. Iffeature_names_in_is not defined, then the following input feature names are generated:["x0", "x1", ..., "x(n_features_in_ - 1)"].If
input_featuresis an array-like, theninput_featuresmust matchfeature_names_in_iffeature_names_in_is defined.
- Returns:
- feature_names_outndarray of str objects
Same as input features.
- get_metadata_routing()[source]#
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- inverse_transform(X)[source]#
Scale back the data to the original representation.
- Parameters:
- X{array-like, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
The rescaled data to be transformed back.
- Returns:
- X_tr{ndarray, sparse matrix} of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Transformed array.
- set_output(*, transform=None)[source]#
Set output container.
See Introducing the set_output API for an example on how to use the API.
- Parameters:
- transform{“default”, “pandas”}, default=None
Configure output of
transformandfit_transform."default": Default output format of a transformer"pandas": DataFrame output"polars": Polars outputNone: Transform configuration is unchanged
New in version 1.4:
"polars"option was added.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
- set_params(**params)[source]#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
Examples using sklearn.preprocessing.RobustScaler#
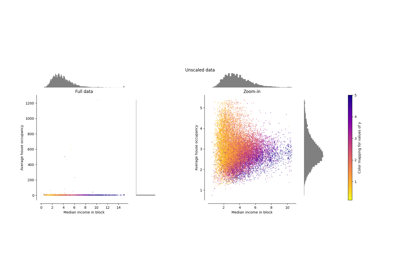
Compare the effect of different scalers on data with outliers